Virtual Clinical Trials Technologies or decentralized and remote trials change clinical research as we know it. These trials optimize new format features which allow participants to participate from home. Virtual Clinical Trials technologies involve the use of a mobile phone, wearables, telemedicine, and other AI forms as aids for data gathering, enhancing patient engagement, and lowering costs. However, several obstacles like lack of technology and regulations may impact virtual clinical trials integration, but still, the trials provide better efficacy, broaden together with foster the patients-first approach for contemporary clinical studies.
What is a virtual clinical trial?
It’s safe to say that such a term has hardly been associated with the word clinical in the past but as clinical research continues to evolve the relevance of this term only grows. Virtual Clinical Trials (VCT) or Virtual clinical research , sometimes referred to as remote or decentralized clinical trials, fundamentally change the way clinical research is performed. This form of clinical research transformative moves fieldwork into the realm of virtual practice, meaning that patients may be included in research from anywhere and can also undergo assessments from any location that is most convenient for them.
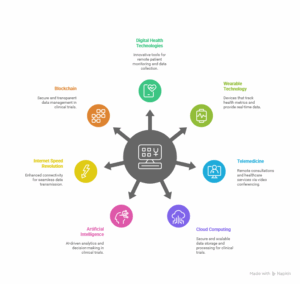
Key Virtual Clinical Trials technologies
Here are the main technologies that support virtual clinical trials.
-
Digital Health Technologies
The advanced equipment in focus for the virtual clinical trials is the advancement of health and technology solutions for data collection and connection of study subjects in distance and different time. These are:
- Mobile Devices and Apps: Smartphones and tablets serve purposes of participant recruitment, eConsent acquisition & electronic clinical outcomes assessment i.e. Data collection.
- Remote Monitoring Devices: These include sensor devices worn on the body that monitor the heart beats blood pressure as well as number of activities facilitating data collection in real time.
-
Wearable Technology
Virtual Clinical Trials can be made possible because of the ability to allow for the non-invasive monitoring of health of the subjects which is made possible using wearables. These can be defined as:
- Smartwatches and fitness bands: These devices gather information on physical activity, sleep, and vital signs.
- Connected Medical Devices: These types include glucose monitors or ECG, and patches that provide health metrics relevant to the overall assessment of trial success or completion.
-
Telemedicine
Telemedicine provides the capacity to conduct visits to patients who cannot attend medical facilities. This aspect entails:
- These consultations are termed virtual visits. Participants can attend the trial staff over video conferencing and do not have to travel as much.
- Home Healthcare Services: Healthcare professional(s) may also visit participants at home and carry out some required assessments or take samples.
-
Cloud Computing
With regard to the platforms, as it can be solicited for integration and analysis of substantial amounts of different trial data, a number of benefits can be highlighted, among which:
- Data Synchronization: All the data reached over the trials is captured in a safe manner so as it can be accessed by the study team at any given time.
- Scalability: With such solutions, trials can be scaled up in size rapidly and reach out to more participants from different parts of the world.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI improves a variety of virtual clinical trials through:
- Data Analysis: Complex mathematical models referred to as machine learning algorithms can scrutinize large volumes of data and pull out useful patterns that can be used to forecast certain outcomes thus leading to better design and execution of trials.
- Participant Recruitment: For patient recruitment, artificial intelligence can be used to determine appropriate participants for a given trial based on their medical history and even increase the efficiency of recruitment.
-
Internet Speed Revolution
The adoption of internet speed revolution promises to enhance virtual trials through:
- High Speed Data Transfers: This allows for fast transfers of large amounts of data such as large files such as imaging or entire health records which significantly improves the standard of remote evaluations provided.
- Enhanced Connectivity: Internet connections allow patients who live in the countryside or in the badlands of the sparsely populated zones to take part with less effort.
-
Blockchain
The incorporation of blockchain technology could further improve the data integrity and security in VCT as follows:
- Data Transparency: It avoids the possibility of unauthorized manipulations of trial information by enabling the monitoring of informed consent.
- Increased Compliance: Participants’ compliance is greatly supported as all trial relations and data submissions are completely protected through the blockchain.
Benefits of Virtual Clinical Trials
Virtual clinical trials (VCT), also known as remote or decentralized clinical trials, leverage digital technologies to conduct clinical research without the need for participants to visit traditional trial sites. This innovative approach offers numerous advantages that enhance the efficiency, accessibility, and inclusivity of clinical research.
-
Improved Patient Participation and Representation
The enhancement of participant access is one of the core advantages of virtual clinical trials. In classic trials, all subjects likely to be recruited for the study are expected to travel to designated centers, hence many sites do not end up recruiting the potential participants, particularly the ones with mobility limitations or residing in other locations. This barrier is consequently removed in virtual trials where people from various ethnic groups including the disabled can stay in their homes and be enrolled in studies. Such diversification of participation increases not only the amount of information obtained but is also consistent with the prevailing guidelines concerning better representation in clinical trials.
-
Enhanced Recruitment and Retention Rates
There is a trend where await trials are easier to recruit than quiescent ones. VCT are decent techniques for quickly and effectively recruiting and screening participants by placing advertisements on websites. Since patients don’t have to traverse, the travel-related dropouts also shrink due to the patients participating from their home. As already seen, VCT does increase the recruitment success of and satisfaction with the participants thus improving retention levels during the entire trial period.
-
Cost Effectiveness
Cost containment is one advantage of virtual clinical trials as they have minimal impact on the costs incurred during clinical trials. Thanks to less travel for participants and no need for physical locations, sponsors stand to make a lot of money savings. As a result of fewer site management requisites, the operational costs are cut down thereby expediting processes and alleviating the administrative workload of the personnel. This attractiveness is even more important in an era when creating new molecules is extremely costly.
-
Gathering and Monitoring Data in the Field or Real Time
The use of the internet, mobile phones and wearable gadgets in the setting of virtual trials permits passive and real time data capture. Researchers do not have to ask subjects to go to a site to assess certain health parameters like heart rate, activity levels and other measurable indices. Such direct data collection not only improves the quality of data in trials but also mitigates the risks of adverse events and compliance breaches subsequent to event occurrence.
-
Enhanced Participation and Empowerment of Patients
Through geo-location enabled systems, virtual trials are able to provide information on a wide range of clinical trials to the patients. Participants are able to view materials related to the research, sign documentations needed and even watch educational videos, which increases their knowledge regarding their pathology, more so the clinical trial. With this level of clarity, it is much easier to interact with patients, which increases their contribution all through the clinical objective’s pursuit.
-
Amending Through Virtual Clinical Trials
There are no major restrictions on the way the trials have to be designed and implemented. For instance, the trial may either be completely virtual, or it may adopt a hybrid approach where some aspects can be virtual, while other parts can be face to face. The spherical features of virtual trials prove to be useful automated backup mechanisms to order managerial encumbrances can be easily implemented in the case of emergencies like diseases outbreaks or natural calamities.
Challenges Faced by Virtual Clinical Trials
-
Technological Limitations
- Access and Digital Literacy: A major constraint is the dependence on technology. There isn’t a uniform availability of internet usage and even among those with access, not every participant can proficiently manage the virtual platforms. As a result, it may lead to the loss of certain segments of the population, especially relative to the elderly or the segments residing in areas with limited internet accessibility.
- Data Security and Privacy Concerns: The very nature of virtual clinical trials raises a host of issues in relation to issues of data security as well as confidentiality of patients’ information. Electronic means of data gathering drive the need to observe a high standard operational safety to prevent information leakage. This type of compliance involves adhering to regulations such as the US HIPAA and the European GDPR and can be quite involved.
-
Engagement and Retention of Participants
- Management of Engagement: Having participants physically present in the scaffold of the researcher is not the case in VCT where most of the interaction is online. This has implications for the will or desire of the participant to be active even in the long run. virtual clinical trials has been tried in some studies using mobile apps and wearable devices. However, CFS has to take care when developing such practices.
- eConsent Issues: The journey of acquiring appropriate information seems to be over when the member electronic centres control, as this leads to members misunderstanding the trial in the absence of direct contact with the personnel responsible for the research. Without any personal contact with the trial workforce, it is possible to have a misapprehension of probably the most important issues of the clinical trial oriented to the new procedure or a medicine.
-
Regulatory Compliance Issues
- Diverse Acceptance Across Regions: Virtual clinical trials regulations still have gaps and progress differently across regions. This inconsistency can hinder multisite trials since sponsors are expected to coordinate the various regulatory needs in the trial planning process.
- Management of data Monitoring and Management: To maintain the data quality and integrity would be the other challenges. There can be issues with data integration where there are a number of different data sources like electronic patient reported outcomes, wearable devices etc. as they are managed poorly across systems leading to increased timelines for the trial and possible errors
-
Operational Challenges
- Restrictions in Trial Types: Certainly, not all clinical trials can be transitioned to a fully simulated site approach, as some trials will require physical contact or some sort of specialized care. Such a limitation means that a fully hybrid model is often the most effective approach, blending both remote work and the physical site where it’s necessary.
- Added Burden of the Study Subjects: In VCTs, the study subjects are more responsible for the self-management of their involvement, for example, having investigational products delivered and performing assessment without clinical staff being actually present. This change can be challenging to overcome for certain people, in particular individuals who need more help.
-
Impediments of Behavior
- Fear of Virtualization: Change is difficult especially when it comes to most of the sponsors and the site staff while implementing virtual tools in running VCTs, such fears are based on traditional means and a tried and tested approach being better. There’s a lot of such inertia which is best handled by educational light and success stories on virtual trial methodologies.
Conclusion
To summarize, virtual clinical trials can be described as the new way of conducting clinical studies. Among the benefits of virtual trials include more potential participants can be accessed, better retention of participants is enabled, and cost savings and faster data collection is made possible. Realizing the power of digital health, wearable technology, telehealth and more, there exists a virtual trials format that is flexible and places the patient at the center which increases patient participation and diversity. On the other hand, In order to harness the full capabilities of virtual clinical trials, many issues including, but not limited to, technological constraints, privacy issues, and compliance with regulatory standards should be dealt with. But even with the challenges, virtual trials hold great promise now and in the future as they have the potential to revolutionize clinical research.
FAQ’s
- What is the main purpose of Virtual Clinical Trials?
Answer: Virtual Clinical Trials (VCTs) center on making research kinder to patients by harnessing digital technologies and remote practices. Rather than asking people to come to a site for every step, Virtual trials let patients enroll, give consent, report symptoms, take tests, and attend study visits from home. Relieving travel and time burdens propels enrollment and keeps participants in the study longer. As a bonus, the research team gets faster, cheaper, and more reliable results from a wider and more diverse group of patients, recorded in real time.
- What percentage of clinical trials are successful?
Answer: Typically, only 10 to 12 percent of molecules that begin clinical trials ever reach the market, the rest being halted at one of the study phases and usually for reasons tied to safety, the desired effect, or practical hurdles that arise later on in the trials.
- Are clinical trials worth the risk?
Answer: Absolutely, clinical trials can be a valuable choice despite any uncertainties. They provide early access to innovative therapies that may not be available to the general public for years, while at the same time pushing our understanding of medicine forward

