Virtual Clinical Trials (VCTs) represent a significant evolution in clinical research methodologies, leveraging digital technologies to facilitate remote participation and data collection. This innovative approach enhances patient engagement by allowing participants to partake in studies from the comfort of their homes, thus overcoming geographical barriers that often limit traditional trials. VCTs not only streamline the research process but also improve data quality and participant diversity, making clinical studies more inclusive and efficient. As the landscape of healthcare continues to evolve, the adoption of Virtual Clinical Trials is poised to reshape how clinical research is conducted, offering numerous opportunities alongside inherent challenges that need careful consideration.
Overview of Virtual Clinical Trial
Virtual clinical trials (VCTs), also referred to as remote or decentralized clinical trials, change the paradigm in the conduct of clinical research. As the name suggests, participants in these trials can partake in these studies right from their homes due to the enabling of digital technologies thus improving ease and access. This overview will define virtual clinical trials, list their advantages, challenges and contemplate their future.
Opportunities in Virtual Clinical Trials
The dynamic field of clinical research is embracing an entirely new concept in the form of virtual clinical trials (VCT). These clinical trials allow studies to be carried out remotely and have many advantages to various stakeholders in the healthcare and pharmaceutical industries. Discussed below are the major advantages that virtual clinical trials offer.
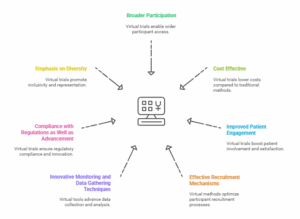
-
Broader Participation
Virtual clinical research help in expanding the geographical scope of the trials and encouraging participation from multiple areas. Owing to this wider reach, it is possible for researchers to obtain data from a larger and more representative segment of the population, which increases the chances of getting more credible findings from the trials and reducing the time spent in getting new treatments approved.
-
Cost Effective
With the virtual execution of the trials, there is a cutback on the physical facilities, movement and physical interactions; hence, costs are cut down considerably. Such clinical trials are directed at the management of sites and logistics; an advantage of implementing cloud-based systems is that organizations can optimize functions and control gross costs.
-
Improved Patient Engagement
Patients appreciate that they are able to take part in trials from their own homes which may improve the chances of them being recruited and remaining in the study. In essence, remote clinical trials enable them to engage in trial activities with less interference to their everyday routines.
-
Effective Recruitment Mechanisms
Recruiting patients for clinical trials can be quite an uphill task. Virtual trials offer a better recruitment proposition as they have the ability to drive digital platforms and call center services up and down depending on the requirement. Such flexibility makes it possible to obtain minimum participants for trials more expeditiously and effortlessly.
-
Innovative Monitoring and Data Gathering Techniques
Owing to the use of wearable devices and remote monitoring tools, virtual trials are capable of performing real time patient health data gathering. This feature not only improves the collectability of data but also makes it possible to keep the patient involved throughout the duration of the trial.
-
Compliance with Regulations as Well as Advancement
Although it is never easy to implement regulatory requirements in a virtual realm, emerging technologies are proving to assist in accomplishing the required guidelines. Increasingly, organizations are pursuing the development of protocols that ensure data protection and confidentiality of patients within the confines of the law.
-
Emphasis on Diversity
There are patients who do not form a part of virtual clinical trials owing to mobility or even geographical limitations. As these trials are conducted remotely, such barriers can be eliminated making the virtual clinical trials more inclusive and in turn ensuring researches improve equity in healthcare.
Challenges in Virtual Clinical Trials
Virtual clinical trials (VCT), also known as the virtual clinical trial model, is defined as one that employs technology to allow clinical trials’ participants to take part in them remotely. These trials have their own set of advantages which include enhanced accessibility and ease of participation for participants. On the flip side, there are multiple challenges that need to be resolved in order to make the “virtual” aspect of the clinical trial as effective as possible.
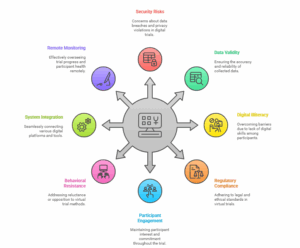
-
Datasets with Security Risks and Privacy Concerns
The issue of security and privacy of clinical trial participants data is one the major concerns when it comes to conducting virtual clinical trials. Data facility limitations which are completely online creates risks of breaches and data theft. It is essential for investigators to provide robust data security measures such as complying to regulatory requirements such as HIPAA, GDPR as well as educating their patients.
-
Keeping The Metric Data Valid
The fidelity of any clinical trial is often dependent on how clinical trial data points are collected, which in the case of virtual clinical trials is significantly impacted by the reliance on patient self-reports and digital therapeutics devices. It is important to keep repeating the instructions on how participants are to log in and report health readings, including elevated cardiovascular statistics in order to remain in compliance with accurate metric reporting.
-
Digital gaps/ Digital Illiteracy: Technology Ownership and Usage
These include technology gaps and technology fluencies. Alden and Zuniga (2020) point out that some elderly or rural communities do not possess devices or internet connections which can in turn form barriers to participation in virtual trials. This gap can negatively affect demographic diversity since not everyone would be able to take part in the trial.
-
Regulatory Compliance
Virtual clinical trials also confront a hard reality of regulatory compliance: Country laws, for instance, telemedicine laws and data protection, are also asymmetrical resulting in researchers having a hard time complying across jurisdictions. This complexity can be a hurdle when it comes to commencing trials as well as operational processes.
-
Participant Engagement and Retention
While efforts made in keeping participants engaged throughout the trial are critical to success, such focus often presents unique difficulties in a virtual format. New methods need to be executed, such as routine virtual updates, interesting digital materials, and even push alerts via desired mobile applications. If participants are not actively engaged in the study, there are likely to be many who will withdraw from it.
-
Behavioral Resistance
The transition from conventional to remote trials encounters resistance and hesitance from stakeholders due to perceived risks. With the new measures that come with new technology, a lot of sponsors and sites tend to resist when there is no clear information on what it will entail. This is in a way a great hindrance to the effective penetration and adoption of remote trials.
-
Integration of Systems
In virtual trials, the success of the study depends on the effective integration of a large number of technological systems. This is an issue that many institutions face which makes data collection and management a cumbersome task. This, in turn, may increase the burden on participants and compliance issues which will have an impact on the outcome of trials.
-
Remote Monitoring Challenges
The issue of quality of monitoring data in the remote setting is another impediment that needs to be addressed. It is important to ascertain that the systems for remote monitoring used in the trial are credible and can provide the needed data in real time in order to protect the integrity of the trial results.
Future Directions and Innovations for Virtual Clinical Trials
From their commencement, virtual clinical trials (VCT) show great potential in integrating technological advancements towards conducting clinical research. Things seem to be changing more importantly, There are several possibilities and directions that would bring about about a revolution in the way virtual clinical trials are carried out
-
Greater Incorporation of Digital Platforms
As VCTs continue to advance, there is a growing trend in the use of digital technologies in the conduct of clinical studies and hence there is emphasis on integrating these technologies in the new VTCs. Some of these technologies include:
- Worn devices: A smartwatch that utilizes devices such as smartwatches can provide metric data continuously without asking subjects to leave their residences to measure them.
- Telemedicine: Patients can perform video call consultations with the healthcare staff, which limits the number of in-person appointments they need to make.
- Remote location assessment: Remote clinical outcome assessment is possible with the use of digital health at homes or local sites of the participants.
-
Hybrid Trial Models
The hybrid model, which is characterized by the coexistence of traditional in-person visits and virtual features, is becoming more widely accepted. Such an approach solves some of the logistical issues while still enjoying the advantages of VCTs. These include:
- Flexibility in participation: Patients have the option to adopt a staggered recruitment strategy. They visit a site to undertake necessary procedures while being able to complete other aspects of the trial from home.
- Improved patient retention: Hybrid models encourage a higher level of participant compliance and less lead to attrition due to less time wasted on traveling and taking into account everyone’s schedule.
-
Increased Patient Diversity and Inclusion
Virtual clinical trials, as a concept, are ideal for increasing the diverse profiles of participants due to the absence of geographical limitations. The participation of all groups has the potential to bring about:
- More representative data: Trials may now recruit subjects from various ethnicities, thereby enhancing the possibility of the findings to be applicable to more people, which has not been the case in clinical trials due to lack of representation.
- Access for underserved populations: People with limitations to their mobility or individuals staying in far-off communities can do so easily hence advancing equity in clinical trials.
-
Supporting Thinking of the Regulations
Virtual trials today, FDA and similar agencies view as prospective opportunities to improve the efficiency of conducting trials and enhancing the patient recruitment pool in the study. In the future, it can be:
- More detailed regulations on digital data capture process: In the future, discussions on the elements of the regulatory framework will address the issues of standardization of principles of remote data and patient’s active source monitoring.
- Make pharmaceuticals look up to VCT methodologies: One way to push virtual clinical trials methodology in different areas would be to provide faster approvals of potential treatments.
-
Artificial Intelligence and machine learning
AI and machine learning applications in virtual clinical trials are anticipated to advance data analysis processes and management of the checkout process of trials as a whole:
- Predictive analytics: The AI predicts the outcomes that should save time and money when running trials.
- Improved patient adherence: communication models can be individualized based on machine learning depending on the characteristics of the patient and improve retention and also patient satisfaction.
-
The former addresses the latter – a patient-focus method for the development of VCT
Virtual trials focus will always be patient-focused and as such they will help define the future of VCTs:
- Adapting trial protocols: Further, protocols can also derive from the needs of the patients, their preferences and their lifestyles hence improving patient experience as a whole.
- Feedback mechanisms: All trials are dynamic in their nature as they are known to modify their intervention but stress the relevance of the study through constant feedback from the participants and adjustments in the trial protocols by the participants in intervention arms throughout the clinical trial.
Conclusion
Lastly, Virtual clinical trials as it stands today is still in its infancy, but its future looks promising and there are a slew of factors driving that future such as hybrid models, advances in digital health, targeted industry regulations, all fostering a faster, cheaper, and personalized solution towards clinical research. Virtual clinical trials in its current form is and will be helpful in advancing clinical research and trials allowing for a more flexible, faster, and efficient process for all parties involved – both for the participants and the researchers.
FAQ’s
- what is a virtual clinical trial?
Answer : A virtual clinical trial runs entirely online, allowing researchers to reach patients through phones, computers, and body sensors rather than through traditional clinic visits. With video calls, smartphone apps, and smartwatches, patients enroll, report symptoms, and send health data from home, authorized staff review the information in real time, and privacy rules keep it secure. Frequent trips to the brick-and-mortar trial site are a thing of the past, minimizing participant burden and expanding access to diverse populations.
2. What is benefits of virtual clinical trials?
Answer: Virtual clinical trials boost recruitment and dropout prevention by letting participants join from home, cutting back on travel to study sites, and overall lowering the patient burden. This design speeds up enrollment, draws in a wider and more representative pool, trims overall costs, and feeds researchers with up-to-the-moment data. By flipping the traditional model, they put patient needs front and center and speed the whole process from design to completion.

